在 RecyclerView 中, 我们可以通过 recyclerView.addItemDecoration() 的方式添加 ItemDecoration ,比如下划线,字母索引等。
使用 自己实现 ItemDecoration ,只需要实现两个方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 static class Example extends RecyclerView .ItemDecoration @Override public void onDraw (Canvas c, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) super .onDraw(c, parent, state); } @Override public void getItemOffsets (Rect outRect, View view, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) super .getItemOffsets(outRect, view, parent, state); } }
其中 onDraw() 提供了一个canvas 用于绘制,getItemOffsets则提供了设置 ItemDecoration 大小的机会,以官方的 DividerItemDecoration 为例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 public class DividerItemDecoration extends RecyclerView .ItemDecoration private void drawVertical (Canvas canvas, RecyclerView parent) canvas.save(); final int left; final int right; if (parent.getClipToPadding()) { left = parent.getPaddingLeft(); right = parent.getWidth() - parent.getPaddingRight(); canvas.clipRect(left, parent.getPaddingTop(), right, parent.getHeight() - parent.getPaddingBottom()); } else { left = 0 ; right = parent.getWidth(); } final int childCount = parent.getChildCount(); for (int i = 0 ; i < childCount; i++) { final View child = parent.getChildAt(i); parent.getDecoratedBoundsWithMargins(child, mBounds); final int bottom = mBounds.bottom + Math.round(child.getTranslationY()); final int top = bottom - mDivider.getIntrinsicHeight(); mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom); mDivider.draw(canvas); } canvas.restore(); } @Override public void getItemOffsets (Rect outRect, View view, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) if (mDivider == null ) { outRect.set(0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ); return ; } if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) { outRect.set(0 , 0 , 0 , mDivider.getIntrinsicHeight()); } else { outRect.set(0 , 0 , mDivider.getIntrinsicWidth(), 0 ); } } } static void getDecoratedBoundsWithMarginsInt (View view, Rect outBounds) final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams(); final Rect insets = lp.mDecorInsets; outBounds.set(view.getLeft() - insets.left - lp.leftMargin, view.getTop() - insets.top - lp.topMargin, view.getRight() + insets.right + lp.rightMargin, view.getBottom() + insets.bottom + lp.bottomMargin); }
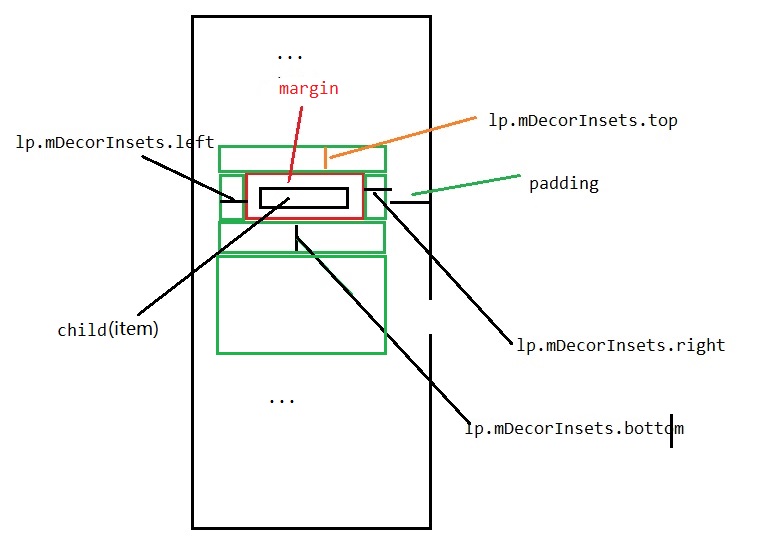
在 drawVertical() 中,先是根据 getClipToPadding() 来判断,要不要把Item绘制到 RecyclerView 的padding 里面,顺便做一个过度绘制的优化,然后调用 getDecoratedBoundsWithMargins() 取得 bottom 的值用于计算绘制的区域,计算的时候用到了 lp.mDecorInsets ,在单个ItemDecoration的情况下,这个值就是在 getItemOffsets() 中设置的 outRect 的值 。需要注意的是,虽然 outRect 的数据结构表示一个矩形,但是这里实际上是表示在child四个方向上的距离值,可以理解为setpadding(left,top,right,bottom),这么命名实在是很让人混乱。。
在这里可以看到,对于简单的分割线,这里只是为每一个 child 绘制了下面的区域 ,其他的区域也都是设置为0.官方的接口其实就只是提供了你绘制的区域(这个还要自己计算)和canvas,让你自己去绘制。关于使用,就是这些了,下面看一下 RecyclerView 是怎么调用这些方法的。
原理 一般来说,作为容器 Container 基本上只需要绘制自己的 background 的, RecyclerView 继承了 ViewGroup 后给我们使用的不仅仅是一个容器,还带了点私货,这个私货就是 itemDecoration , 对于每一个 item , RecyclerView 新定义了 layoutParam,在自己的layoutparams 中保存了一个 mDecorInsets 的变量,用来记载 itemDecoration 的范围。在 measure,layout 的时候都会考虑到这些值进行测量和布局,最后在ondraw里面把 canvas 交给开发者自己去实现。不过它留的接口传的参数实在是怪异,需要知道详情才知道怎么去绘制。
由于child的测量和绘制也是由LayoutManager去自定义实现的,但是系统也提供了LinearLayoutManager等实现,这里以LinearLayoutManager为例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public void measureChildWithMargins (View child, int widthUsed, int heightUsed) final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); final Rect insets = mRecyclerView.getItemDecorInsetsForChild(child); widthUsed += insets.left + insets.right; heightUsed += insets.top + insets.bottom; final int widthSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(getWidth(), getWidthMode(), getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin + widthUsed, lp.width, canScrollHorizontally()); final int heightSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(getHeight(), getHeightMode(), getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin + heightUsed, lp.height, canScrollVertically()); if (shouldMeasureChild(child, widthSpec, heightSpec, lp)) { child.measure(widthSpec, heightSpec); } } public void layoutDecoratedWithMargins (View child, int left, int top, int right,int bottom) final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); final Rect insets = lp.mDecorInsets; child.layout(left + insets.left + lp.leftMargin, top + insets.top + lp.topMargin, right - insets.right - lp.rightMargin, bottom - insets.bottom - lp.bottomMargin); }
可以看到都是把 mDecorInsets 考虑在里面了的,如果我们自定义LayoutManager,也需要考虑到对itemDecoration的支持,不然可能会出现显示问题。
关于 itemDecoration 的绘制,这个就在 RecyclerView 的 ondraw() 函数里面,非常简单:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public void onDraw (Canvas c) super .onDraw(c); final int count = mItemDecorations.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < count; i++) { mItemDecorations.get(i).onDraw(c, this , mState); } }
如果有多个 ItemDecoration , 会依次绘制,这个需要每一个 ItemDecoration 自己计算好绘制的区域。
另外一个方法 getItemOffset() 的唯一调用处:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Rect getItemDecorInsetsForChild (View child) { final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); if (!lp.mInsetsDirty) { return lp.mDecorInsets; } if (mState.isPreLayout() && (lp.isItemChanged() || lp.isViewInvalid())) { return lp.mDecorInsets; } final Rect insets = lp.mDecorInsets; insets.set(0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ); final int decorCount = mItemDecorations.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < decorCount; i++) { mTempRect.set(0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ); mItemDecorations.get(i).getItemOffsets(mTempRect, child, this , mState); insets.left += mTempRect.left; insets.top += mTempRect.top; insets.right += mTempRect.right; insets.bottom += mTempRect.bottom; } lp.mInsetsDirty = false ; return insets; }
这里仅仅是取了每一种 ItemDecoration 类的 getItemOffsets() 传进来的 rect 数据,然后依次叠加,只有一种 ItemDecoration 的时候,rect 其实就是 mDecorInsets 的值。